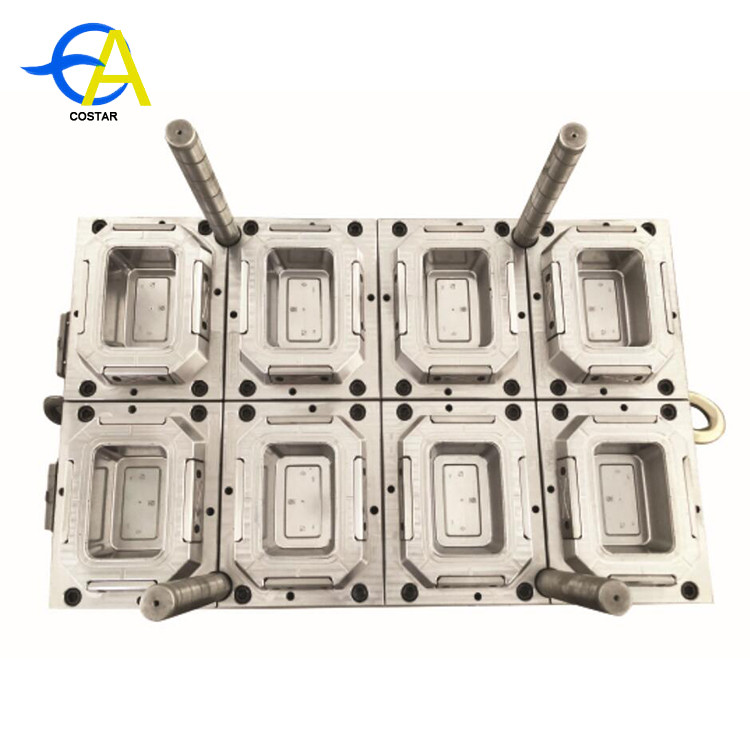
Material selection of plastic mold
- Share
- Issue Time
- Apr 30,2021
Summary
Due to the development of the plastics and plastic molding industry, the quality requirements for plastic molds are becoming higher and higher. Therefore, the failure of plastic molds and their influencing factors have become an important research topic.
1. Working conditions of plastic molds
Due to the development of the plastics and plastic molding industry, the quality requirements for plastic molds are becoming higher and higher. Therefore, the failure of plastic molds and their influencing factors have become an important research topic. The main working parts of plastic molds are molding parts, such as punches, concave molds, etc., which form the cavity of the plastic mold to form various surfaces of plastic parts and directly contact the plastic, and withstand pressure, temperature, friction and corrosion, etc. effect.
2. Analysis of failure causes of plastic mold materials
Generally, mold manufacturing includes mold design, material selection, heat treatment, machining, debugging and installation. According to the investigation, among the factors of mold failure, the material and heat treatment used in the mold are the main factors affecting the service life. From the perspective of total quality management, the factors that affect the service life of the mold cannot be measured as the sum of polynomials, but should be the product of multiple factors. In this way, the advantages and disadvantages of mold materials and heat treatment appear special throughout the mold manufacturing process. important.
From the analysis of the common phenomenon of mold failure, plastic molds can cause wear failure, local deformation failure and fracture failure during the service process. The important failure modes of plastic molds can be divided into wear failure, local plastic deformation failure and fracture failure.
3. Plastic mold steel performance requirements. With the rapid development of the manufacturing industry, plastic molds are indispensable tools in plastic molding processing, and their proportion in the total mold output is increasing year by year. With the development and continuous production of high-performance plastics, The types of plastic products are increasing day by day, and their uses continue to expand. Products are becoming more sophisticated, large-scale, and more complex. The molding production is developing at a high speed, and the working conditions of the mold are becoming more and more complicated.
1) Wear and corrosion of cavity surface
The plastic melt flows in the mold cavity under a certain pressure, and the solidified plastic part comes out of the mold, which will cause friction on the molding surface of the mold and cause wear. The root cause of plastic mold wear and failure is the friction between the mold and the material. However, the specific form of wear and the wear process are related to many factors, such as the pressure, temperature, material deformation speed and lubrication condition of the mold during the working process. When the materials and heat treatment used in the plastic mold are unreasonable, the surface hardness of the plastic mold cavity is low, and the wear resistance is poor, which is expressed as: the size of the cavity surface is out of tolerance due to wear and deformation; the roughness value becomes higher due to napping , The surface quality deteriorates. Especially when solid materials are used to enter the plastic mold cavity, it will aggravate the wear of the cavity surface. In addition, when the plastic is processed, components such as chlorine and fluorine are heated to decompose corrosive gases HC1 and HF, which cause corrosion and wear on the surface of the plastic mold cavity, resulting in failure. If there is abrasion damage at the same time as the wear, the plating layer or other protective layer on the surface of the cavity is destroyed, which will promote the corrosion process. The cross action of the two types of damage accelerates corrosion-wear failure.
2) Plastic deformation failure
Pressure and heat on the surface of the plastic mold cavity can cause plastic deformation failure, especially when small molds are working on large-tonnage equipment, they are more likely to produce overload plastic deformation. The material used in the plastic mold has insufficient strength and toughness, and low deformation resistance; another reason for plastic deformation failure is that the hardened layer on the surface of the mold cavity is too thin, the deformation resistance is insufficient, or the working temperature is higher than the tempering temperature, which causes phase change and softening. , And make the mold fail early.
3) Fracture
The main cause of fracture is structural stress, thermal stress or insufficient tempering due to the structure and temperature difference. At the service temperature, the retained austenite is transformed into martensite, causing local volume expansion, and the structure generated inside the mold Caused by stress.
The working conditions of plastic molds are different from those of cold stamping dies. Generally, they must work at 150°C-200°C. In addition to being subjected to a certain pressure, they also have to withstand temperature. There are multiple failure modes for the same mold, and multiple damages may occur even on the same mold. From the failure mode of the plastic mold, it is very important to select plastic mold materials and heat treatment reasonably, because they are directly related to the service life of the mold. Therefore, steel for plastic molds should meet the following requirements:
1) Heat resistance
With the advent of high-speed molding machinery, plastic products run faster. Since the molding temperature is between 200-350℃, if the plastic fluidity is not good and the forming speed is fast, the surface temperature of the mould part will exceed 400℃ in a very short time. In order to ensure the precision and small deformation of the mold during use, the mold steel should have high heat resistance.
2) Sufficient wear resistance
With the expansion of the use of plastic products, it is often necessary to add inorganic materials such as glass fiber to plastics to enhance plasticity. Due to the addition of additives, the fluidity of the plastic is greatly reduced, resulting in mold wear, so it is required to have good Abrasion resistance.
3) Excellent machinability
Most plastic molding molds require certain cutting processing and fitter repairs in addition to EDM. In order to prolong the service life of the cutting tool, the work hardening is small during the cutting process. In order to avoid mold deformation and affect accuracy, it is hoped that the residual stress of machining can be controlled to a minimum.
4) Good thermal stability
The shape of the parts of the plastic injection mold is often complicated and difficult to process after quenching. Therefore, materials with good thermal stability should be selected as far as possible.
5) Mirror processing performance
The surface of the cavity is smooth, and the molding surface needs to be polished into a mirror surface, and the surface roughness is lower than Ra0.4μm to ensure the appearance of the plastic molded part and facilitate demolding.
6) Heat treatment performance
In the mold failure accident, the accident caused by heat treatment is generally 52.3%, so that the heat treatment occupies an important position in the entire mold manufacturing process, and the quality of the heat treatment process has a greater impact on the quality of the mold. Generally require small heat treatment deformation, wide quenching temperature range, low overheating sensitivity, especially greater hardenability and hardenability, etc.
7) Corrosion resistance
During the forming process, corrosive gas may be released and heated to decompose corrosive gas, such as HC1, HF, etc., which corrode the mold, and sometimes the mold is rusted and damaged at the air flow passage mouth. Therefore, the mold steel is required to have good corrosion resistance.
4. New plastic mold steel
Generally, plastic molds are made of normalized 45 steel or 40Cr steel after quenching and tempering. Plastic molds with higher hardness requirements are made of steel such as CrWMn or Crl2MoV. For plastic molds with higher working temperature, hot work mold steel with high toughness can be selected. In order to meet the higher requirements for dimensional accuracy and surface quality of plastic cavities, a series of new mold steels have recently been developed.
1) Carburized plastic mold steel
Carburized plastic mold steel is mainly used for cold extrusion molding of plastic molds with complex cavities. This type of steel has a relatively high carbon content.
Plastic mould
Plastic mould
Low, often add element Cr, while adding appropriate amount of Ni, Mo and v, the function is to improve hardenability and carburizing ability, in order to facilitate cold extrusion forming, this kind of steel must have high plasticity and low deformation resistance in the annealed state , Annealing hardness ≤ 100HBS. Carburizing and quenching and tempering treatment are carried out after cold extrusion, and the surface hardness can reach 58---62HRC. There are special steel grades for this kind of steel abroad, such as 8416 in Sweden, P2 and P4 in the United States and so on. In China, 12CrNi3A and 12Cr2Ni4A steel, 20Cr2Ni4A are often used, which have good wear resistance, no collapse and surface spalling, and the life of the mold is improved. The elements cr, Ni, Mo, and V in the steel increase the hardness and wear resistance of the carburized layer and the strength and toughness of the core.
2) Pre-hardened plastic mold steel
The carbon content of this type of steel is 0.3% -0.55%, and the commonly used alloying elements are Cr, Ni, Mn, v and so on. In order to improve its machinability, elements such as s and ca are added. Several typical plastic mold steels Y55CrNiMn-MoVS (SMI) have been developed through research and introduction, which are S-containing free-cutting plastic mold steels developed in China. Its characteristic is that the pre-hardened delivery hardness is 35_40 HRC, which has better cutting performance. Processability, no heat treatment after processing, can be used directly. Adding Ni solid solution strengthening and increasing toughness, adding Mn and S to form a free-cutting phase MnS; adding Cr, Mo, V, increasing the hardenability of steel 8Cr2S steel is sufficient for free-cutting precision mold steel.
3) Age-hardening plastic mold steel
Maraging steel with low cobalt, no cobalt, and low nickel has been developed. MASI is a typical maraging steel. After 8150C solution treatment, the hardness is 28-32HRC, and it is mechanically processed and then aged at 4800C. During aging, Ni3Mo, Ni3Ti and other intermetallic compounds are folded out to make the hardness reach 48-52 HRC. Steel has high strength and toughness, small dimensional changes during aging, and good weld repair performance. However, steel is expensive and not very popular in China.
4) Corrosion resistant plastic mold steel
Plastic products made of polyvinyl chloride (Pvc) and ABS plus flame-resistant resin are decomposed during the forming process.
Plastic mould
Plastic mould
Corrosive gas will corrode the mold. Therefore, plastic mold steel is required to have good corrosion resistance. There are two types of corrosion-resistant plastic mold steels commonly used abroad: martensitic stainless steel and precipitation hardening stainless steel. Foreign ones include STVAX (4Crl3) and A SSAB-8407 of Sweden ASSAB. [2]
